When considering dietary supplements for enhancing beauty and health, biotin and collagen often come to the forefront of the discussion. As a person who values wellness, I’ve taken an interest in understanding how these supplements work and their benefits.
Biotin, a B vitamin also known as vitamin H, plays a vital role in supporting metabolism On the flip side, collagen, which comes in pill or powder form, a protein found abundantly in the body, is essential for providing structural support to skin, bones, and connective tissues.
While both biotin and collagen have unique functions, they share a common ground in contributing to a healthy appearance.
- Biotin supports metabolism and improves the health of hair, skin, and nails
- Collagen provides structural support and maintains skin elasticity
- Both supplements contribute to a healthy appearance and have distinctive roles
With that in mind, let us discuss these and more important things you need to know about biotin and collagen.
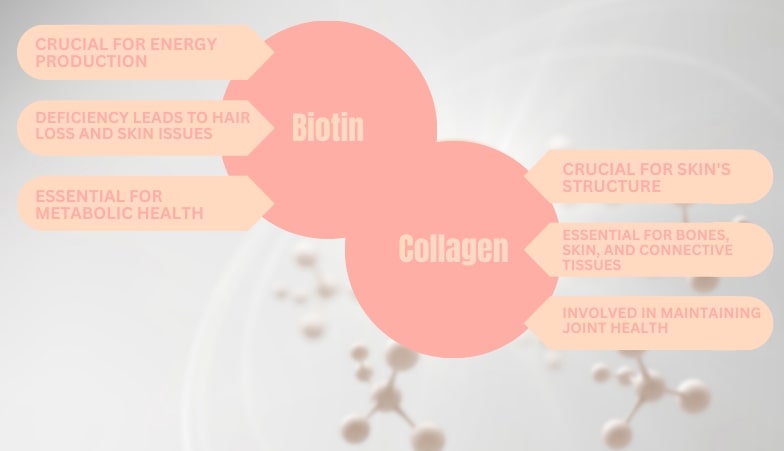
Biotin Versus Collagen
| Nutrient | Description | Key Functions/Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Biotin (Vitamin B7) | Water-soluble vitamin, important in fatty acid and amino acid synthesis. | Crucial for energy production; affects skin, hair, and nail health. Deficiency leads to hair loss and skin issues. |
| Collagen | Abundant protein in the body, essential for bones, skin, and connective tissues. | Varies in types; vital for skin, tendons, cartilage, and organ structure. |
Dietary Sources for Biotin and Collagen
I find biotin in a variety of foods I may include in my diet, such as eggs, nuts, legumes, and liver. In contrast, dietary sources of collagen are primarily animal-based; they include meat, fish, bone broth, and gelatin.
Harvard study states: In food, collagen is naturally found only in animal flesh like meat and fish that contain connective tissue. However, a variety of both animal and plant foods contain materials for collagen production in our own bodies.
For vegetarians or those looking to boost their collagen intake without consuming animal products, vitamin C is crucial for collagen synthesis, so including vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits and leafy greens in one’s diet can be beneficial.
The Role in the Body
Both biotin and collagen play pivotal roles in physiology as well. Biotin is essential for metabolic health, whereas collagen is the scaffolding of the human body, maintaining the integrity of skin, the strength of bones, and the flexibility of joints.
Hamid M Said’s research reveals the following: It is well know now that biotin plays important roles in a variety of critical metabolic reactions in the cell, and thus, is essential for normal human health, growth and development.
Their roles in hair growth, nail health, and bone health cannot be overstated. Importantly, I acknowledge that their interplay ensures the health and functionality of critical biological systems, including joints, ligaments, tendons, and blood vessels.
Benefits and Functions
In this section, I cover the distinct benefits and functions of biotin and collagen, focusing on how they influence skin, hair, and nails, as well as their roles in bone and joint health. You can expect different benefits depending on the variant, either bovine or marine.
Impact on Skin and Aging
I understand that skin’s elasticity and its appearance as I age are significantly influenced by the proteins it’s made of. Collagen, which is crucial for maintaining skin’s structure, tends to decrease naturally over time, leading to wrinkles and decreased skin elasticity.
Oral collagen peptides supplementation has been shown to result in improved skin elasticity and hydration, which can combat signs of aging. Biotin doesn’t directly impact collagen production, but it contributes to overall skin health by supporting the function of enzymes responsible for maintaining a healthy complexion.
Hair and Nails Enhancement
Hair and nails are constantly growing, and they need the right nutrients to stay strong and healthy.
Biotin is essential for the health and growth of hair and nails.Collagen also plays a role here. Evidence to show that using oral collagen can provide benefits in this regard is emerging, although research continues.
Imashi Fernando states: “Biotin may support hair growth in people whose hair thinning or loss occurs due to a biotin deficiency. Other vitamin deficiencies may also affect the health of your hair”.
Supporting Bone and Joint Health
Bones and joints support the body throughout life, and their health is imperative.
- Collagen is a major part of bones and cartilage, giving them structure and strength. It’s also involved in maintaining joint health, and studies suggest that collagen supplementation can bring relief to conditions such as joint pain.
- Biotin, while not directly linked to bone health, is still significant for overall health, and maintaining adequate levels ensures that all the bodily functions that support bone and joint health are optimized.
According to Reema Patel, Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body. It is found in the bones, skin, muscles, and tendons. Doctors use collagen in wound healing techniques. Collagen also features in many cosmetic preparations for the skin.
Supplementation and Dosage
When selecting a biotin supplement or collagen peptides, it’s crucial to consider purity, ingredient sources, and the presence of fillers or preservatives. For healthy skin, look for products with added vitamin C, zinc, and copper, which may aid in collagen synthesis.
The optimal intake of biotin is typically 30 to 100 micrograms daily for adults and teenagers, while collagen dosage varies, often recommended between 2.5 to 15 grams per day.Mayoclinic study reveals that the optimal intake for different age groups is following:
-
Adults and teenagers—30 to 100 micrograms (mcg) per day.
-
Children 7 to 10 years of age—30 mcg per day.
-
Children 4 to 6 years of age—25 mcg per day.
-
Children birth to 3 years of age—10 to 20 mcg per day.
Be aware that high doses of biotin can interfere with lab tests, and while collagen is generally safe, some may experience mild digestive side effects.
Remember, mixing it properly is a must. Clinical studies have shown that biotin can support healthy hair and nails, while collagen supplementation may enhance skin elasticity and joint health. For instance, products containing hydrolyzed fish collagen are linked to skin health improvements.
For both biotin and collagen, co-ingestion with certain nutrients can boost absorption.
According to ScienceDirect, raw egg whites can impede biotin absorption due to the presence of avidin.
Once again, the timing can be decisive. Attaining nutrients from a balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and fruits is essential, but aging, pregnancy, and lifestyle factors like smoking can increase the necessity for supplementation.
For vegetarians, finding the right supplement form is key since most collagen derives from animal sources. Of course, you will need to go through a wide array of factors before you make the purchase.
Precautions and Interactions
It’s vital to be aware of potential allergic reactions and contraindications, as well as interactions with various medications, which may affect overall health.
Potential Allergic Reactions
The National Library of Medicine states that both biotin and collagen supplements have the capacity to induce allergic reactions in some users. Skin rashes, itching, or eczema may be signs of an allergy, particularly if they occur soon after beginning supplementation.
- Biotin is a B vitamin crucial for tissue maintenance and supporting enzyme functions important to metabolism. When taken in high doses, it is generally considered safe, but over-supplementation may lead to unwanted effects.
- Collagen, a protein found in various body tissues, is also typically safe for consumption.
I advise anyone with a history of allergies or disease related to these sources to consult with a healthcare provider before adding collagen to their regimen.
Interactions with Medications
Medications may interact with biotin or collagen supplements. For instance, biotin can potentially affect laboratory tests and falsely skew results, especially thyroid-related tests. Individuals on medications for thyroid disease must be particularly cautious.
To quote the American Thyroid Association: Most commonly, biotin use can result in falsely high levels of T4 and T3 and falsely low levels of TSH, leading to either a wrong diagnosis of hyperthyroidism or that the thyroid hormone dose is too high.
For my part, ensuring transparent communication with healthcare providers about any supplemental biotin intake is crucial. This ensures that test results are interpreted correctly. Collagen supplements, on the other hand, are not generally known to interact with medications.
Nevertheless, due to the role of collagen in tissue repair and health, I consider it prudent for individuals taking anticoagulant medication to seek medical advice, as supplementary proteins may have a mild effect on blood clotting processes.
Optimizing Biotin and Collagen Intake
In my pursuit of a balanced approach to supplementing my diet with biotin and collagen, I’ve focused on natural sources and understanding how my body utilizes these nutrients.
Balancing Through Diet
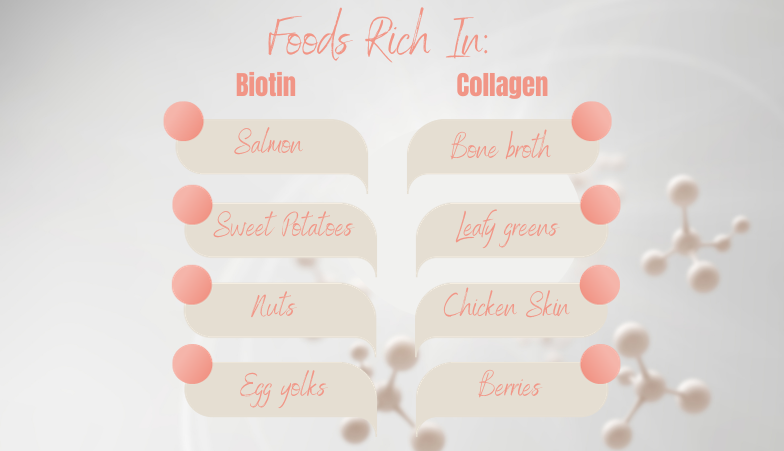
I prioritize biotin and collagen intake by including a variety of foods in a diet. For biotin, I turn to salmon, sweet potatoes, and nuts, which are not only rich in biotin but also provide healthy fats and protein. This approach supports overall health and contributes to a balanced diet.
Collagen sources, on the other hand, are different. They are primarily found in animal products, particularly in protein-rich foods such as chicken skin, bone broth, and gelatin.
For a more plant-based approach, I ensure that a diet includes vegetables and fruits that support collagen production, like leafy greens and berries that provide the necessary vitamins and nutrients for collagen synthesis.
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Biotin | Salmon, Sweet Potatoes, Nuts | Supports metabolism |
| Collagen | Chicken Skin, Bone Broth, Leafy Greens | Aids in skin and joint health |
Absorption and Utilization
My focus on absorption and utilization of biotin and collagen is as crucial as my intake. Biotin functions as a coenzyme in carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Therefore, a balanced intake of these macronutrients is essential for optimal biotin activity within my body.
Factors such as gut health are critical for biotin absorption. To enhance collagen absorption, I pay attention to both the digestion of protein and my intake of vitamin C which is vital for the synthesis of collagen.
Ensuring that my diet is not too high in sugar and refined carbohydrates is also important because these can interfere with collagen’s ability to repair the skin. Powder form is the go-to choice for those seeking higher absorption, especially when compared to pills. Another solid option would be the liquid variant.
FAQs
The Bottom Line
I find that both biotin and collagen offer unique benefits for health.
Studies suggest that biotin supplementation may not significantly affect hair loss in individuals without a deficiency, as indicated by a systematic review. On the other hand, collagen supplements demonstrate a potential for improving skin elasticity and possibly aiding in wound healing.I emphasize that individual needs vary, and taking either supplement should be based on personal health goals and nutritional requirements.
It’s also important for me to point out that supplements should complement a balanced diet and lifestyle, and it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Related Posts:
- Can You Take Too Much Biotin and How Much is Enough?…
- 7 Mini Habits That Will Help You Become One Percent…
- 7 Best Biotin for Hair Growth in 2024- Top Picks +…
- Magnesium vs Melatonin: Which Is Better and Why Are…
- Physician's Choice vs Garden of Life - Which…
- Benefits of Rose Tea: Sip Your Way to Better Health