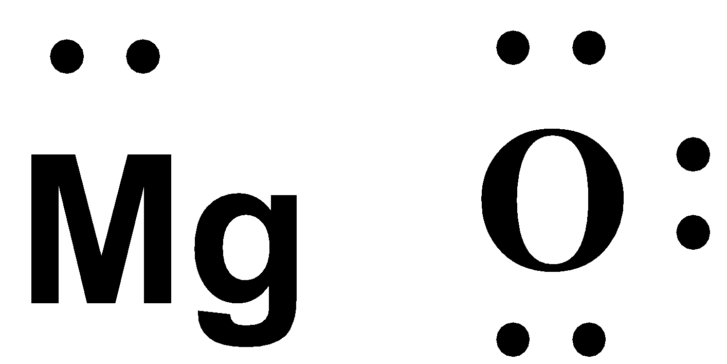Magnesium is essential for many biological processes, such as energy production, muscle contraction, nerve transmission, and bone formation. But how many valence electrons does magnesium have, and why does it matter?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, which can participate in the formation of chemical bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons determines the chemical properties and reactivity of an element, as well as its ability to form compounds with different elements.
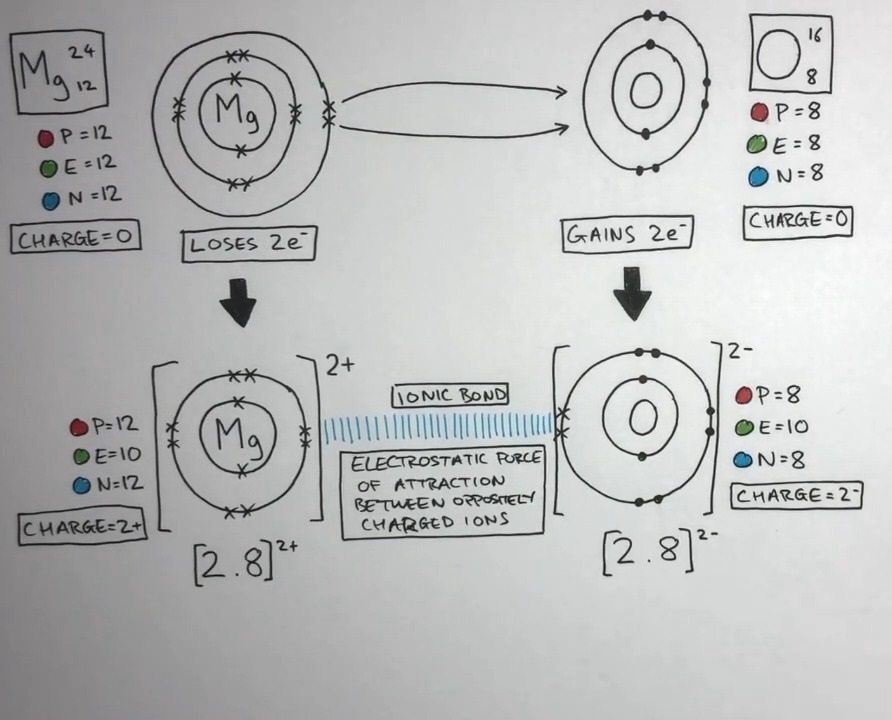
Magnesium has 12 electrons, 12 protons and 12 neutrons that can vary. The first two shells are completely filled with eight electrons each, while the third shell has six electrons and the fourth shell has two electrons.
The crucial part is that it has 2 valence electrons, both in the 3s orbital. This means that magnesium can lose these two electrons to achieve a stable configuration of eight valence electrons, which is the same as the noble gas neon. I will provide more details about valence electrons and relation to Magnesium in the following blog post.
What are Valence Electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, which can participate in the formation of chemical bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons determines the chemical properties and reactivity of an element, as well as its ability to form compounds with different elements.
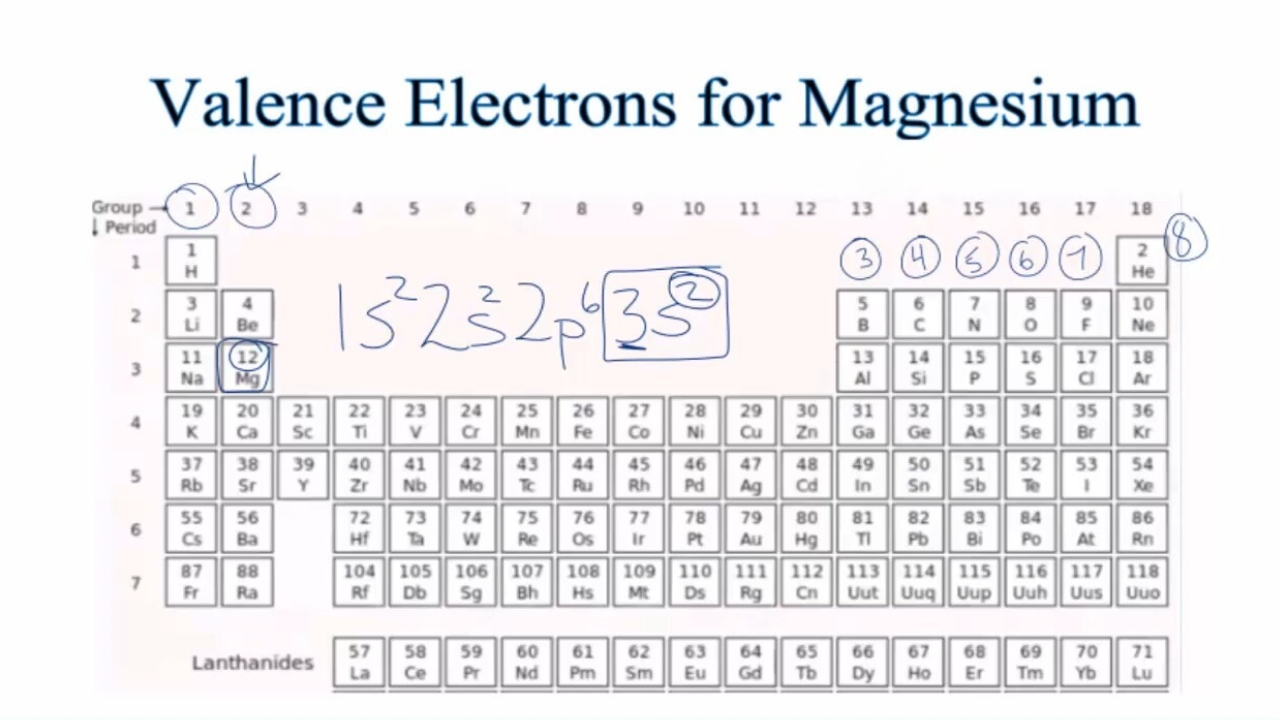
The valence electrons of an atom can be represented by using the electron configuration notation, which shows the distribution of electrons in different shells and subshells. For example, the electron configuration of magnesium is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2.
The first shell has two electrons in the s subshell, the second shell has two electrons in the s subshell and six electrons in the p subshell, the third shell has two electrons in the s subshell, and the fourth shell has no electrons.
The electrons in the first two shells are called core electrons, and they do not participate in chemical bonding. The electrons in the third and fourth shells are called valence electrons, and they are the ones that can form bonds with other atoms.
How Does Magnesium Form Bonds with Other Elements?
It can form two types of bonds with other elements: ionic bonds and covalent bonds.
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are formed when atoms transfer electrons from one to another, creating oppositely charged ions that attract each other. Magnesium can form ionic bonds with elements that can gain two electrons, such as oxygen, chlorine, and sulfur. These elements become negatively charged ions, or anions, with a charge of 2-.
For example, It can react with oxygen to form magnesium oxide (MgO), in which each atom loses two electrons and each oxygen atom gains two electrons. The resulting compound is a neutral ionic compound, with a ratio of one magnesium ion to one oxygen ion.
| Compound | Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|
| MgO | Magnesium oxide | A white solid that is used as a refractory material, a catalyst, and a component of cement |
| MgCl2 | Magnesium chloride | A colorless crystalline salt that is used as a source of magnesium, a de-icing agent, and a coagulant |
| MgSO4 | Magnesium sulfate | A white powder that is used as a fertilizer, a laxative, and a component of bath salts |
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons, creating a molecule. Magnesium can form covalent bonds with elements that can share electrons, such as carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen.
These elements have a high electronegativity, which means that they have a strong attraction for electrons. In a covalent bond, two atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons, creating a molecule.
For example, it can react with carbon to form magnesium carbide (MgC2), in which each magnesium atom shares two electrons with a carbon atom, forming a triple bond. The resulting compound is a gray solid that is used as a source of acetylene gas.
| Compound | Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|
| MgC2 | Magnesium carbide | A gray solid that is used as a source of acetylene gas |
| MgH2 | Magnesium hydride | A white solid that is used as a hydrogen storage material and a reducing agent |
| Mg3N2 | Magnesium nitride | A yellow solid that is used as a fertilizer and a catalyst |
Additional Facts About Valence Electrons and Magnesium
The valence electrons are important for its chemical reactivity, as they are the ones that can be transferred or shared with other atoms to form bonds. This element tends to lose its two valence electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration, similar to the noble gas neon.
This makes magnesium a highly reactive metal that can form ionic compounds with nonmetals, such as halogens, oxygen, and sulfur. The valence electrons of magnesium are also involved in its physical properties, such as its electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and melting point.
Magnesium has a high electrical conductivity because its valence electrons are free to move in the metallic lattice, allowing the flow of electric current. It also has a high thermal conductivity because its valence electrons can transfer heat energy through the metal. This essential element has a low melting point because its valence electrons are weakly held by the nucleus, making it easy to overcome the metallic bonds.
The valence electrons of magnesium are also essential for its biological functions, as they are involved in the formation of magnesium ions (Mg2+), which are vital for many cellular processes. Magnesium ions are the second most abundant cations in living cells, after potassium ions.
The ions play important roles in the synthesis of DNA and RNA, the activation of enzymes, the regulation of calcium levels, the transmission of nerve impulses, and the contraction of muscles. Magnesium ions are also found in chlorophyll, the green pigment that allows plants to perform photosynthesis.
FAQs
How do you find the number of valence electrons of an element?
You can find the number of valence electrons of an element by looking at its position in the periodic table. The elements in the same group (column) have the same number of valence electrons. For example, magnesium is in group 2, so it has two valence electrons.
Why is magnesium a metal?
Magnesium is a metal because it has few valence electrons (two) that it can easily lose to form positive ions. Metals tend to lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration, similar to the noble gases. Metals also have metallic bonds, which are the attraction between positive ions and free electrons in a metal.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds are formed when atoms transfer electrons from one to another, creating oppositely charged ions that attract each other. Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons, creating a molecule. Ionic bonds are usually formed between metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds are usually formed between nonmetals.
What is the electron dot structure of magnesium?
The electron dot structure of magnesium is a symbol of the element surrounded by dots that represent its valence electrons. For example, the electron dot structure of magnesium is Mg with two dots, one on each side.
What is the oxidation state of magnesium?
The oxidation state of magnesium is the charge of the magnesium ion after it loses or gains electrons. Magnesium usually has an oxidation state of 2+, which means that it loses two electrons and becomes a positive ion. The oxidation state of magnesium can be written as Mg<sup>2+</sup>.
What are some common uses of magnesium?
Magnesium is used for many purposes, such as making alloys, fireworks, flares, batteries, medicines, and dietary supplements. Magnesium is also important for human health, as it is involved in many biochemical reactions and processes. Magnesium deficiency can cause symptoms such as muscle cramps, fatigue, and irregular heartbeat.
Conclusion
Magnesium is an element that has two valence electrons. These electrons can make bonds with other elements in different ways. Magnesium can form ionic compounds, covalent compounds, and metallic bonds. It is important for many things, such as industry, agriculture, medicine, and life.
Related Posts:
- How Many Neutrons Does Magnesium Have? Find Out How…
- How Many Strains Should a Probiotic Have? - An Insight
- What is Breathwork Meditation & Its Benefits? A Deep…
- How Does Family Life Affect Mental Health? Building…
- How Does Spravato Therapy Affect the Brain?
- Magnesium vs Melatonin: Which Is Better and Why Are…